Innovative Sustainable Architecture: Building a Greener Future
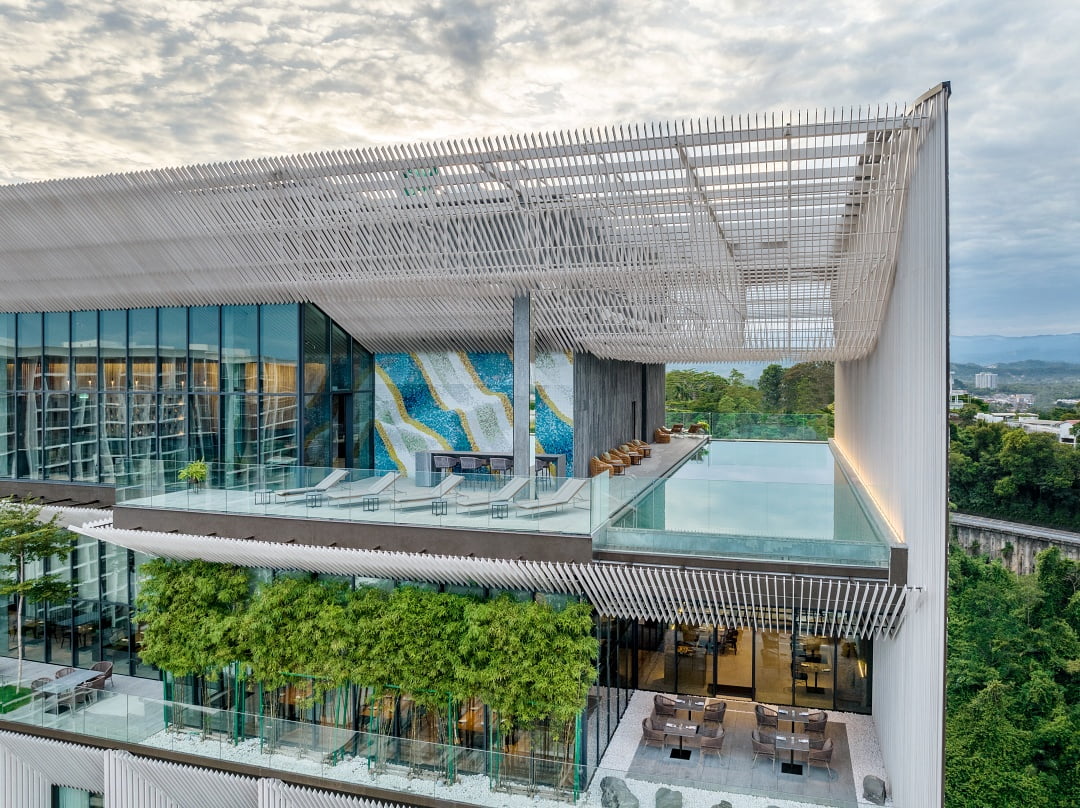
In the ever-evolving landscape of architecture, a profound shift towards sustainability is taking center stage. “Sustainable architecture” is not just a buzzword; it is a guiding principle that architects and designers are adopting to create structures that are in harmony with the environment. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of innovative sustainable architecture.
-Decoding Sustainable Architecture
What is sustainable architecture?
At its core, sustainable architecture seeks to reduce the negative environmental impact of buildings by efficiently using energy, materials and space. This approach goes beyond traditional design, aiming to strike a balance between functionality, aesthetics and environmental responsibility.
Designing for longevity
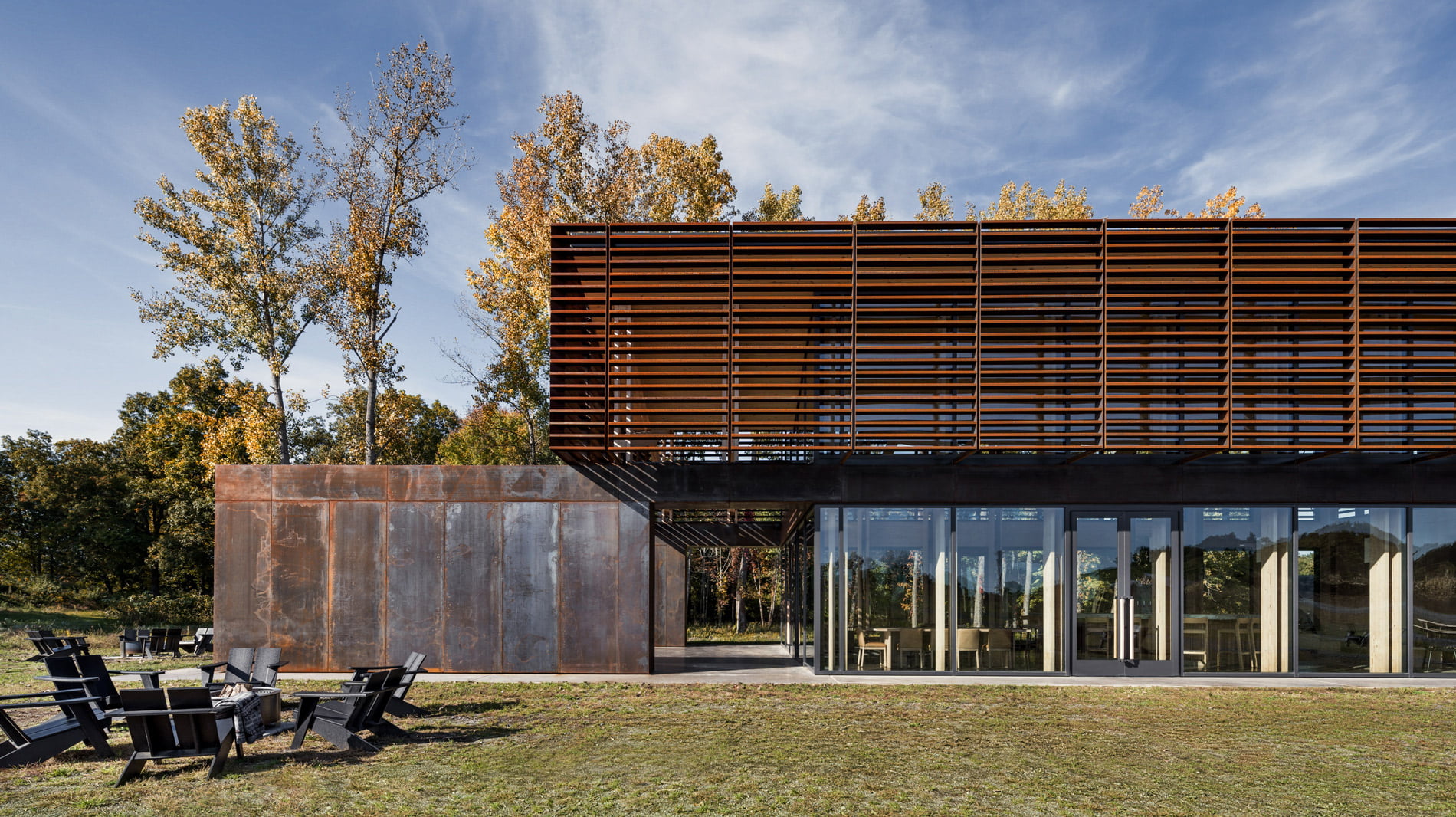
Sustainable architecture prioritizes longevity and durability. Buildings are designed with the future in mind, using materials that will stand the test of time, reducing the need for frequent renovations and resource-intensive construction processes.
-Fundamentals of Sustainable Architecture
Energy-efficient design
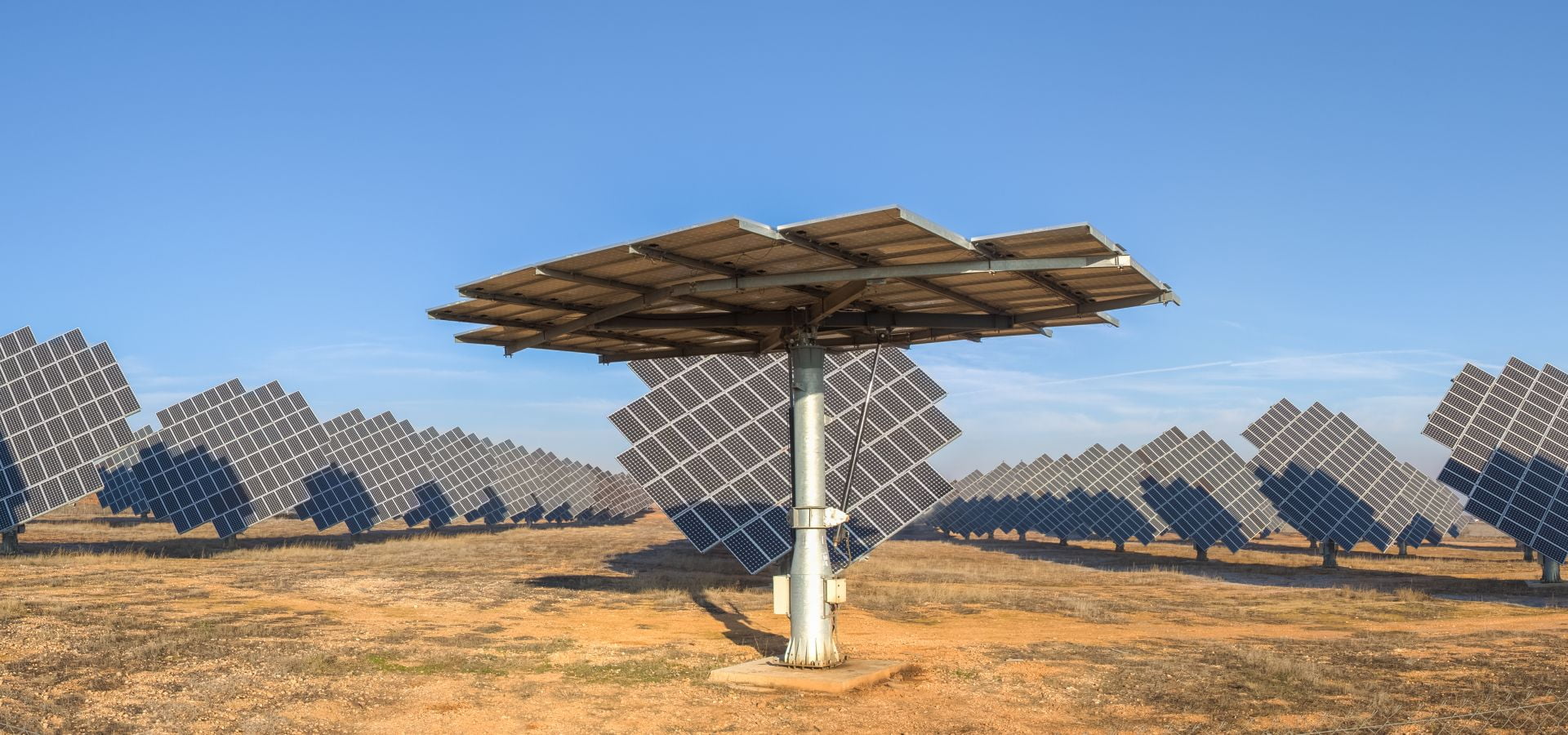
One of the fundamental principles is the integration of energy-efficient design. Architects take advantage of natural light, ventilation systems, and renewable energy sources to create structures that consume minimal energy and, in some cases, generate their own electricity.
Eco-friendly materials
Sustainable architecture supports the use of eco-friendly materials, promoting the idea that every element of a building should make a positive contribution to the environment. From recycled steel to reclaimed wood, architects are exploring innovative materials that reduce their carbon footprint.
Water conservation strategies
Water scarcity is a global concern, and sustainable architecture addresses it through innovative water conservation strategies. Rainwater harvesting, groundwater systems and efficient irrigation are some examples of how architects are reducing water consumption in their designs.
-Exemplars of Sustainable Architecture
The Crystal: A Beacon of Sustainable Innovation
Situated in London, The Crystal is a shining example of Sustainable Architecture. This eco-friendly building utilizes a combination of renewable energy sources, efficient insulation, and sustainable materials to achieve a minimal environmental impact.
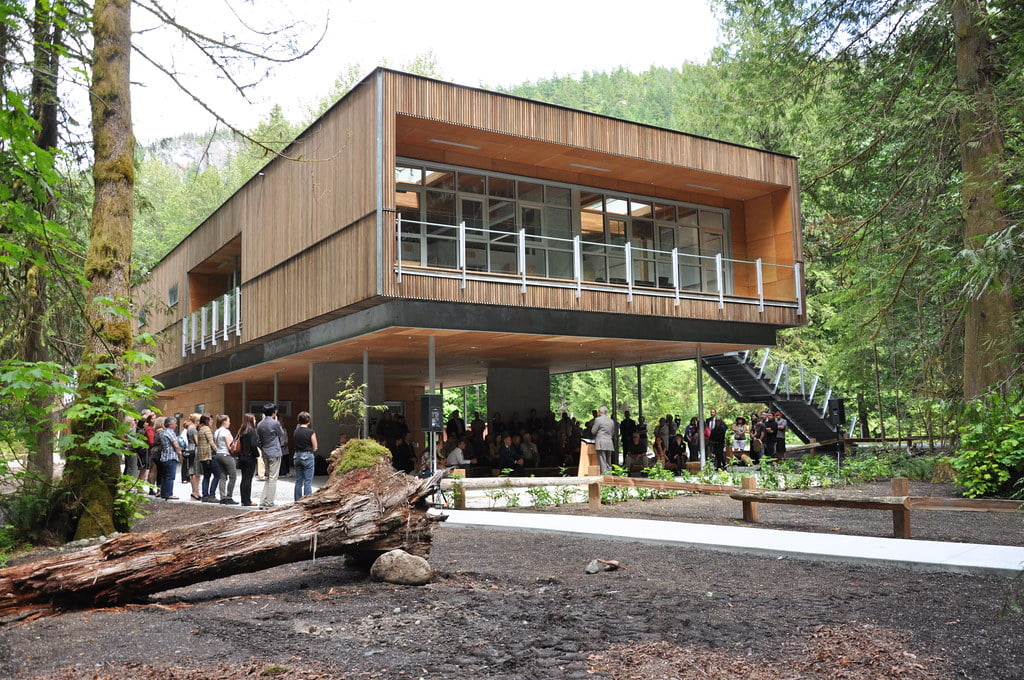
The Green School: Nurturing Sustainability in Education
The Green School in Bali demonstrates how Sustainable Architecture can extend beyond commercial buildings. This institution is a testament to sustainable living, incorporating bamboo structures, renewable energy, and permaculture principles.
-Challenges and Triumphs in Sustainable Architecture
Overcoming Challenges
While the benefits of Sustainable Architecture are evident, challenges such as higher initial costs and resistance to change remain. However, architects and advocates are working together to overcome these hurdles and make sustainable practices more accessible.
Triumphs and Transformations
The successes in Sustainable Architecture are inspiring transformations globally. From energy-efficient skyscrapers to eco-friendly homes, architects are proving that sustainable design can be both innovative and aesthetically pleasing.
-Future Horizons of Sustainable Architecture
Technological Advancements
As technology evolves, so does Sustainable Architecture. The future promises even more groundbreaking innovations, with developments in smart building systems, sustainable materials, and energy-efficient technologies.
Global Collaboration for a Sustainable Tomorrow
Sustainable Architecture is a collective effort. Architects, policymakers, and communities must collaborate to create a sustainable future. The global movement towards sustainable practices is an encouraging sign that positive change is on the horizon.
-In conclusion
Sustainable architecture is not just a trend; It is a responsibility towards the planet and future generations. By adopting innovative designs, eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient practices, we pave the way for a more sustainable and harmonious co-existence with the environment. Let’s celebrate the architects and designers who are shaping a future where beauty and sustainability go hand in hand.
FAQ:
-What is sustainable architecture?
Sustainable architecture, also known as green or eco-friendly architecture, is an approach to designing buildings and structures with a primary focus on reducing negative environmental impact while promoting positive social and economic outcomes. The goal of sustainable architecture is to create structures that are environmentally responsible, resource-efficient, and flexible, meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Key principles and characteristics of sustainable architecture include:
Energy efficiency:
Sustainable buildings are designed to use energy more efficiently, often including features such as solar panels, energy-efficient lighting, and smart building systems. It aims to reduce overall energy consumption and dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Eco-Friendly Materials:
Choosing materials with low environmental impact is a fundamental aspect of sustainable architecture. This includes using recycled, reclaimed or rapidly renewable materials and avoiding harmful environmental impacts.
Water conservation:
Sustainable architecture considers water efficiency by incorporating features like rainwater harvesting, greywater systems and water-efficient fixtures. This helps reduce water consumption and the environmental impact of water use.
Site selection and planning:
Selecting a site with minimal environmental impact and harmoniously integrating the building with its surroundings is a key principle. This may include preserving natural vegetation, considering the orientation of the building for optimal sunlight, and minimizing disruption to ecosystems.
Waste Reduction:
Sustainable architecture emphasizes construction waste reduction and encourages recycling. This involves designing for building deconstruction and re-use of materials, reducing the environmental impact associated with the end of a building’s life.
Biophilic design:
Integrating natural elements into the built environment is a way to enhance occupant well-being and connect people with nature. This may include incorporating plants, natural light, and nature scenes into the design.
Adaptive reuse and renovation:
Instead of demolishing existing structures, sustainable architecture often promotes the adaptive reuse of buildings. This approach minimizes waste and conserves the energy embodied in existing structures.
Community and social considerations:
Sustainable architecture extends beyond the building to consider its impact on the community. This involves creating spaces that promote social interaction, accessibility and a positive impact on the local community and economy.
Lifecycle assessment:
Assessing the environmental impact of a building throughout its lifecycle is an important aspect of sustainable architecture. This includes evaluating the environmental costs associated with construction, operation, maintenance, and ultimately demolition or reconstruction.
Sustainable architecture is an emerging field that responds to advances in technology, materials, and increasing awareness of environmental challenges. It aims to address the critical issues of climate change, resource depletion and environmental degradation by promoting responsible and thoughtful design practices.
-What is sustainable architecture design?
Sustainable architectural design refers to the process of creating buildings and structures with a focus on reducing negative environmental impacts, optimizing resource use, and promoting long-term environmental, social, and economic sustainability. Sustainable architectural design integrates principles and strategies that address environmental challenges such as climate change, resource depletion, and ecosystem degradation. Here are the key elements of sustainable architectural design:
Site Selection and Planning:
Choose sites that have minimal environmental impact and consider factors such as solar orientation, wind patterns and the local ecosystem.
Plan for efficient land use, preserving green spaces and minimizing disruption to natural habitats.
Energy efficiency:
Prioritize energy-efficient design by incorporating proper building orientation, maximizing natural light, and effective insulation.
Integrate renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems to reduce reliance on non-renewable energy.
Water conservation:
Implement water-efficient design by incorporating technologies like rainwater harvesting, greywater systems and low-flow fixtures.
Use landscaping strategies that reduce water consumption, such as selecting native plants and efficient irrigation systems.
Material Selection:
Choose durable and eco-friendly materials with low environmental impact, considering factors such as embodied energy, recyclability and sustainability.
Incorporate recycled and reclaimed materials to reduce demand for virgin resources.
Waste Reduction and Recycling:
Design for minimal construction waste by promoting on-site recycling and reuse of materials.
Consider remodelability and adaptability in the design to facilitate future renovation or reuse of the building.
Biophilic Design:
Integrate natural elements into the built environment, such as incorporating plants, natural light and nature views to enhance the well-being of residents.
Create spaces that foster connections between occupants and the natural world.
Adaptive Reuse and Refurbishment:
Whenever possible prefer adaptive re-use of existing structures rather than demolishing them, conserving the energy embodied in the existing building.
Renovate buildings to meet modern sustainability standards, upgrade systems and materials for better efficiency.
Community and Social Considerations:
Design spaces that foster social interaction, community engagement and inclusivity.
Consider the wider impact of the building on the local community, supporting economic growth and social well-being.
Life cycle assessment:
Conduct a life cycle assessment to evaluate the environmental impact of a building from construction to operation to eventual demolition or dismantling.
Consider the long-term durability and maintenance requirements of materials and systems.
Sustainable architectural design is an iterative and holistic process that involves collaboration between architects, engineers, builders and other stakeholders. Its objective is to create a built environment that is not only environmentally responsible but also contributes positively to the well-being of its occupants and the surrounding community.